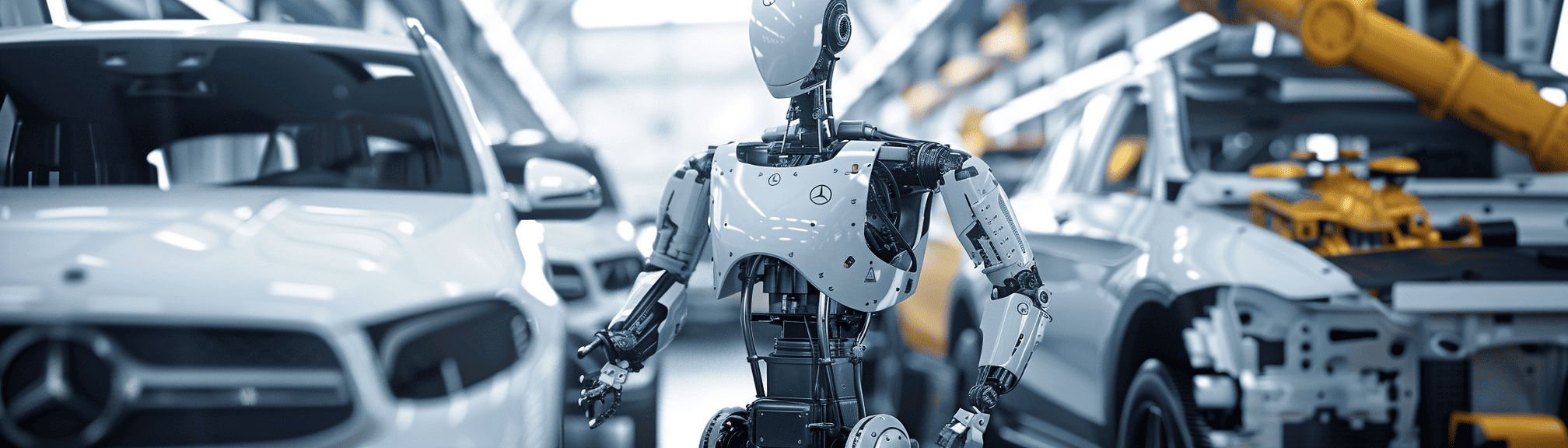
Mercedes-Benz Explores Automation in Manufacturing with Bipedal Robots
Mercedes-Benz, the renowned automotive manufacturer, has recently ventured into a new realm of advanced robotics to enhance its manufacturing process.
The company has partnered with Apptronik, a leading robotics firm, to explore potential applications of bipedal robots in automating physically challenging and repetitive tasks. The initiative aims to leverage cutting-edge technology to improve efficiency and productivity while addressing the industry’s labour shortages.
This strategic collaboration follows BMW’s similar announcement earlier this year, which indicates a growing trend in the automotive industry toward integrating advanced robotics into traditional manufacturing processes. Mercedes-Benz’s move toward automation signifies its commitment to innovation and technological advancement.
The Humanoid Robot at the Forefront of Automotive Manufacturing
At the heart of this pioneering initiative is Apollo, a 160-pound bipedal robot developed by Apptronik. At five feet eight inches tall, Apollo can lift objects weighing up to 55 pounds, making it ideal for automating physically challenging tasks in the manufacturing process.
Mercedes-Benz is exploring potential Apollo applications, such as inspecting and delivering components to human workers on the production line. While the agreement’s specifics remain undisclosed, the pilot programme represents a significant step towards automating manufacturing tasks without extensive redesign of existing facilities.
The Impact of Advanced Robotics on the Automotive Industry
Apptronik asserts that integrating humanoid robots like Apollo could be a game-changer for vehicle manufacturers. The company’s approach centres on automating physically demanding, repetitive and monotonous tasks that are increasingly difficult to fill with reliable human workers.
Mercedes-Benz has already initiated a trial of an undisclosed number of Apollo robots at a factory in Hungary, which has been grappling with labour shortages for several years. The move is a response to the increasing migration of workers to Western Europe, which has sparked concerns among automotive manufacturers, including Audi and Mercedes-Benz.
Jörg Burzer, Mercedes’ production chief, highlighted the potential of robotics to address labour gaps, particularly in low-skill, repetitive and physically demanding work. He stated, “This is a new frontier, and we want to understand the potential both for robotics and automotive manufacturing to fill labour gaps… and to free up our highly skilled team members on the line to build the world’s most desirable cars.“
The Future of Robotics in Manufacturing
Introducing robots like Apollo in the automotive manufacturing process is not an isolated trend. Other humanoid robots, such as Tesla’s Optimus robot and the Figure 01 robots that BMW is trialling at its South Carolina manufacturing facility, are also making waves in the industry. Moreover, bipedal robots such as Agility Robotics’ “Digit” are being piloted in Amazon’s US warehouses, indicating a broader shift towards automation across various sectors.
As companies like Mercedes-Benz continue to explore the potential of advanced robotics in manufacturing, this technological revolution will surely shape the future of the automotive industry.
Integrating robots like Apollo into traditional manufacturing processes could significantly enhance productivity, efficiency and quality, marking a new era in automotive manufacturing.